Classical Mechanics - Physics LibreTexts
Classical mechanics describes the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars and galaxies. If the present …
Classical mechanics describes the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars and galaxies. If the present state of an object is known it is possible to predict by the laws of classical mechanics how it will move in the future (determinism) and how it has moved in the past (reversibility)
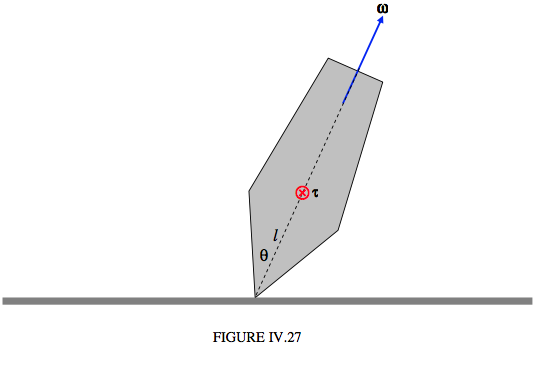
4.10: The Top - Physics LibreTexts

Difference Between Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Mechanics

11.1: Rolling Motion - Physics LibreTexts, PDF, Rotation Around A Fixed Axis

Essential Graduate Physics - Statistical Mechanics [4]
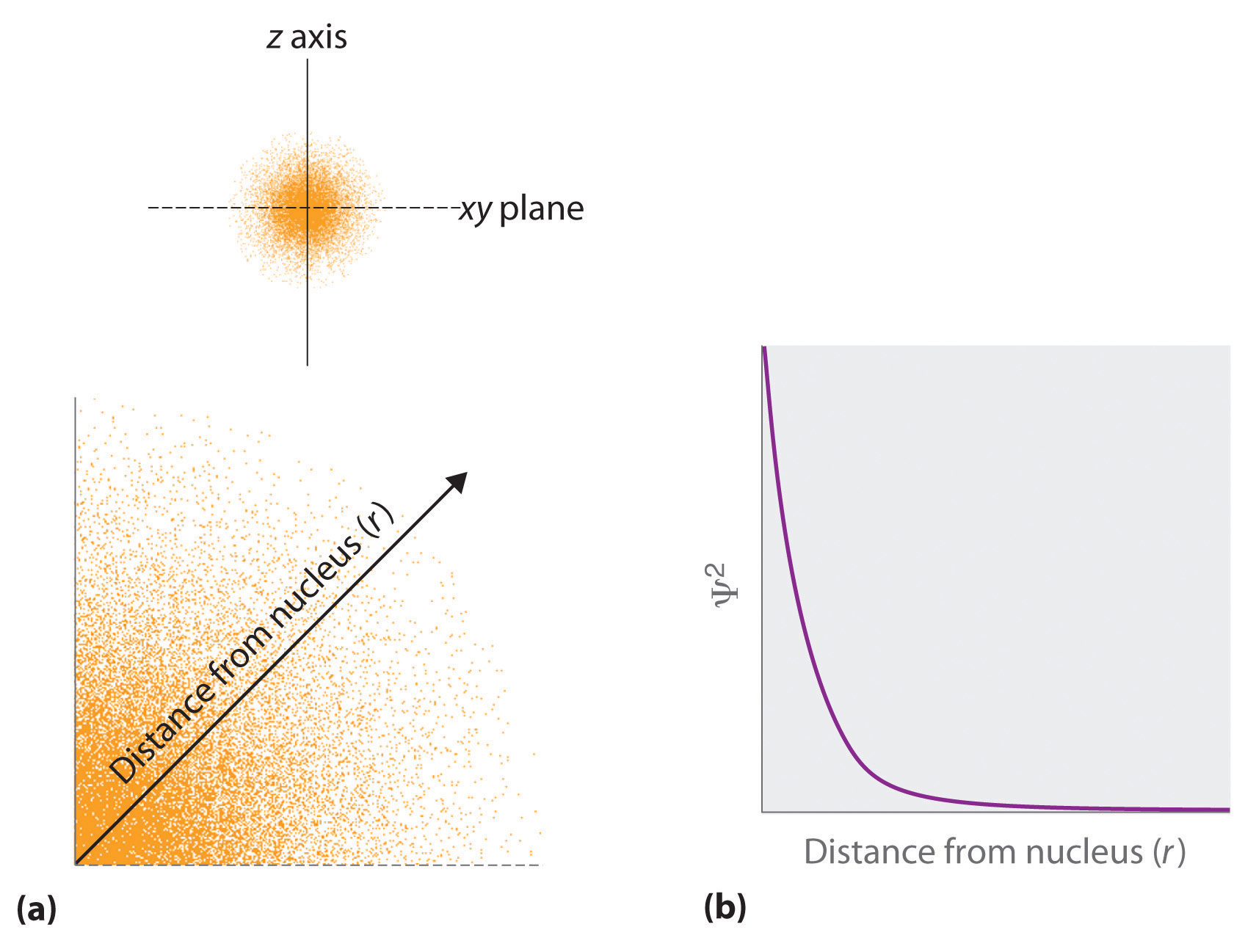
3.5 Quantum Mechanics and The Atom – Chemistry LibreTexts – Chemistry Fundamentals
UCD: Physics 9HA – Classical Mechanics - Physics LibreTexts
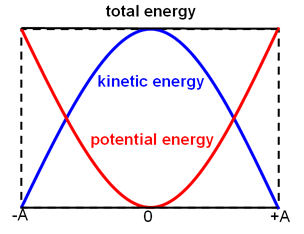
Physics - Classical Mechanics - Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion

Advanced Quantum Mechanics

Physics - Classical Mechanics - Work and Kinetic Energy — Steemit
Epilogue - Physics LibreTexts
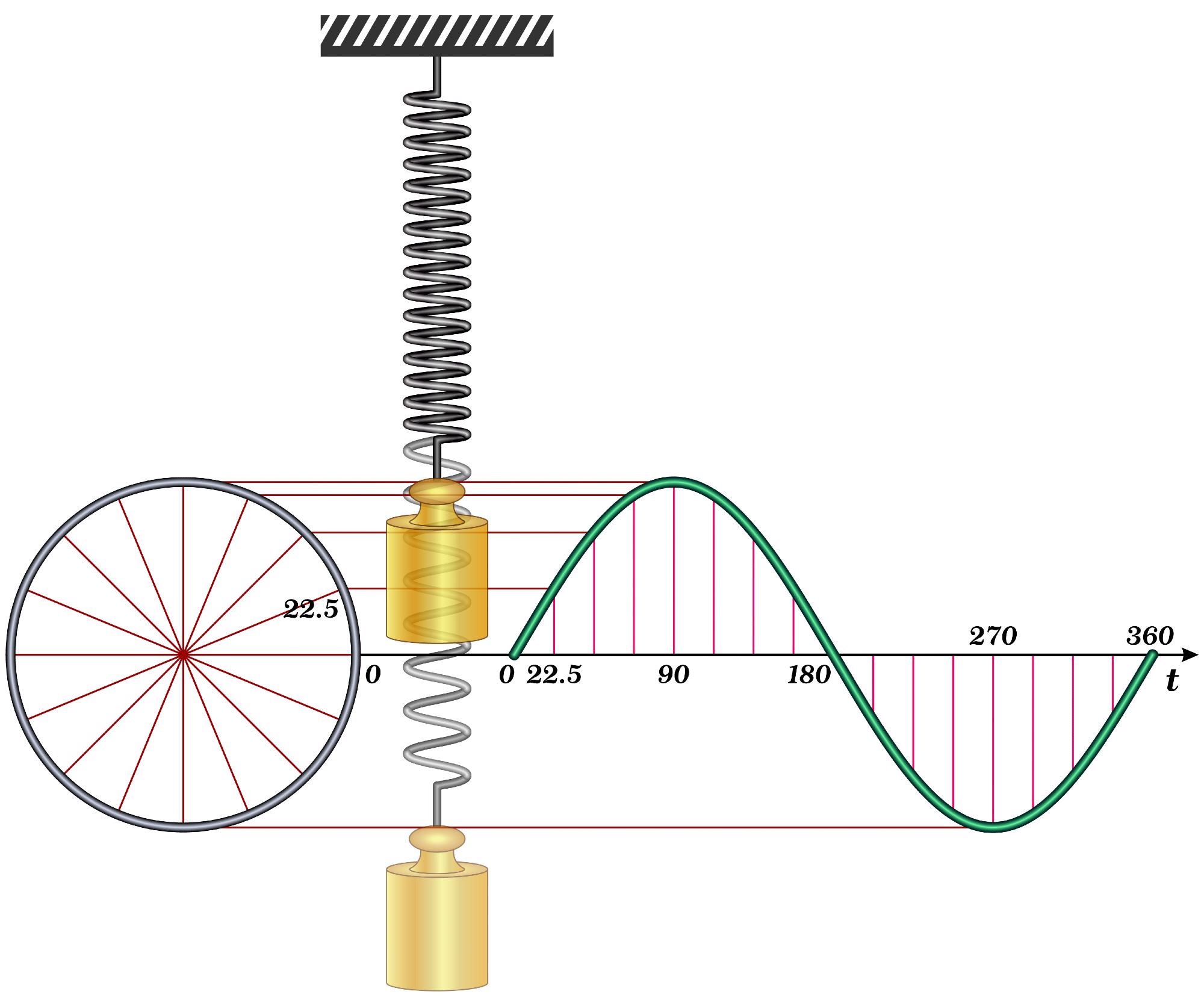
An Overview of Harmonic Oscillators
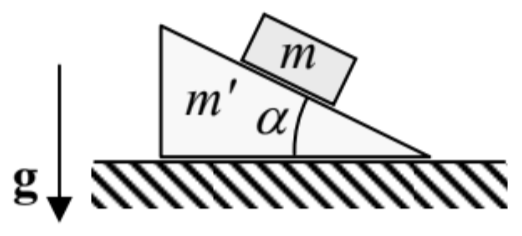
10.5: Exercise Problems - Physics LibreTexts

Hamilton's equations, mathematics







