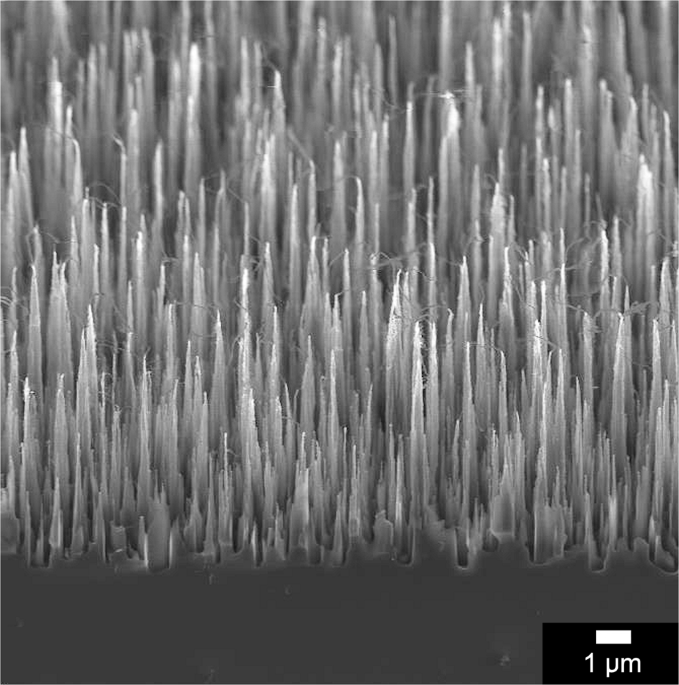
Studies of Black Diamond as an antibacterial surface for Gram

IJMS, Free Full-Text

JFB, Free Full-Text

Bacterial attachment and biofilm formation on surfaces are reduced by small-diameter nanoscale pores: how small is small enough?
Studies of black silicon and black diamond as materials for antibacterial surfaces - Biomaterials Science (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C8BM00107C

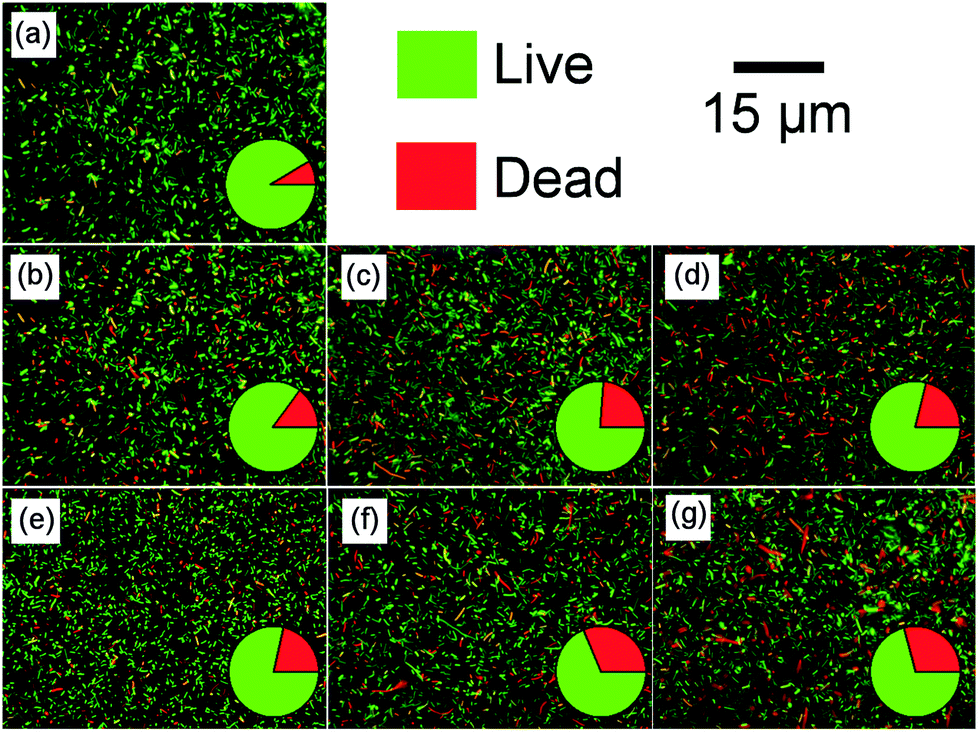
Antibacterial action of graphene-coated Titanium sheets. (a) Live/dead

Morphology-dependent antibacterial properties of diamond coatings

Antibacterial effects of nanopillar surfaces are mediated by cell impedance, penetration and induction of oxidative stress

Antibacterial efficiency of carbon dots against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: A review - ScienceDirect
Impacts of a Nano-Laponite Ceramic on Surface Performance, Apatite Mineralization, Cell Response, and Osseointegration of a Polyimide-Based Biocomposite. - Document - Gale OneFile: Health and Medicine
Impacts of a Nano-Laponite Ceramic on Surface Performance, Apatite Mineralization, Cell Response, and Osseointegration of a Polyimide-Based Biocomposite. - Document - Gale OneFile: Health and Medicine

Studies of Black Diamond as an antibacterial surface for Gram Negative bacteria: the interplay between chemical and mechanical bactericidal activity

Effect of NDM treatment of bacteria on their metabolic activity

Biomimetics, Free Full-Text

Effect of medium and aggregation on antibacterial activity of nanodiamonds - ScienceDirect
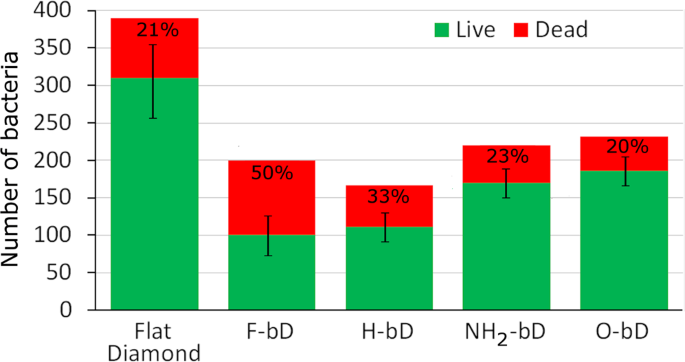
Studies of Black Diamond as an antibacterial surface for Gram Negative bacteria: the interplay between chemical and mechanical bactericidal activity



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/negative-photo-illusion-56a791df3df78cf7729736f2.jpg)



