CD24+/CD38- as new prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer, Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine
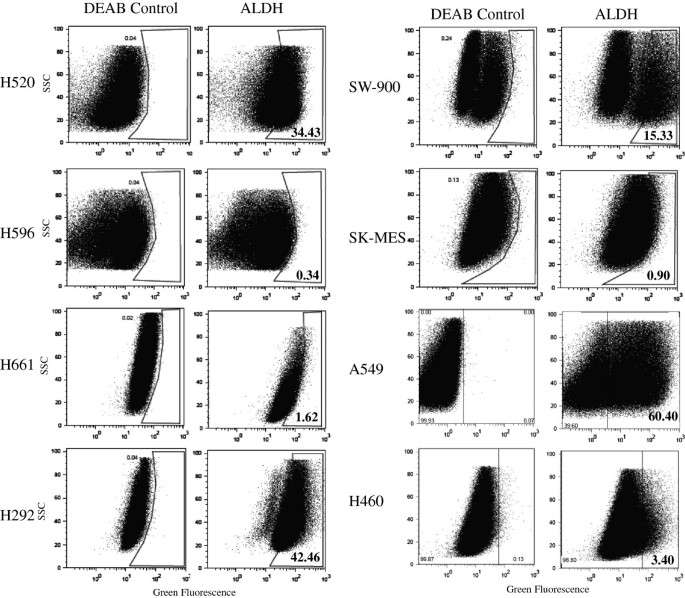
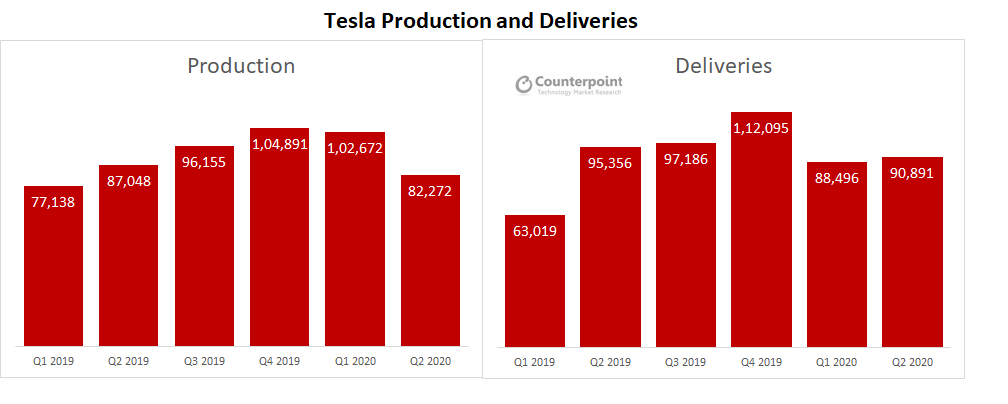
Background Lung cancer is the leading cause of death among cancers in the world. The annual death toll due to this disease exceeds the combined deaths caused by colon, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. As a result, there has been a tremendous effort to identify new biomarkers for early detection and diagnosis of lung cancer. Methods In this study we report the results of screening a panel of eight non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines originating from different subtypes of lung cancer in an attempt to identify potential biomarkers unique to this disease. We used real-time polymerase chain reaction and flow cytometry techniques to analyze the expression of ALDHA1, EpCAM, CD133, CD24, and CD38 in this panel. Results We demonstrate for the first time that the majority of NSCLC cells do not express levels of CD38 that would qualify it as a new biomarker for the disease. In contrast, we found that CD24 is over-expressed in 6 out of 8 of the cell lines. The combined CD24+/CD38-/low phenotype was detected in 50% of the cell lines that are also positive for CD133 and EpCAM. Conclusions We report that CD24+/CD38-/low signature could potentially be used as a new biomarker for the early detection of NSCLC.
IJMS, Free Full-Text

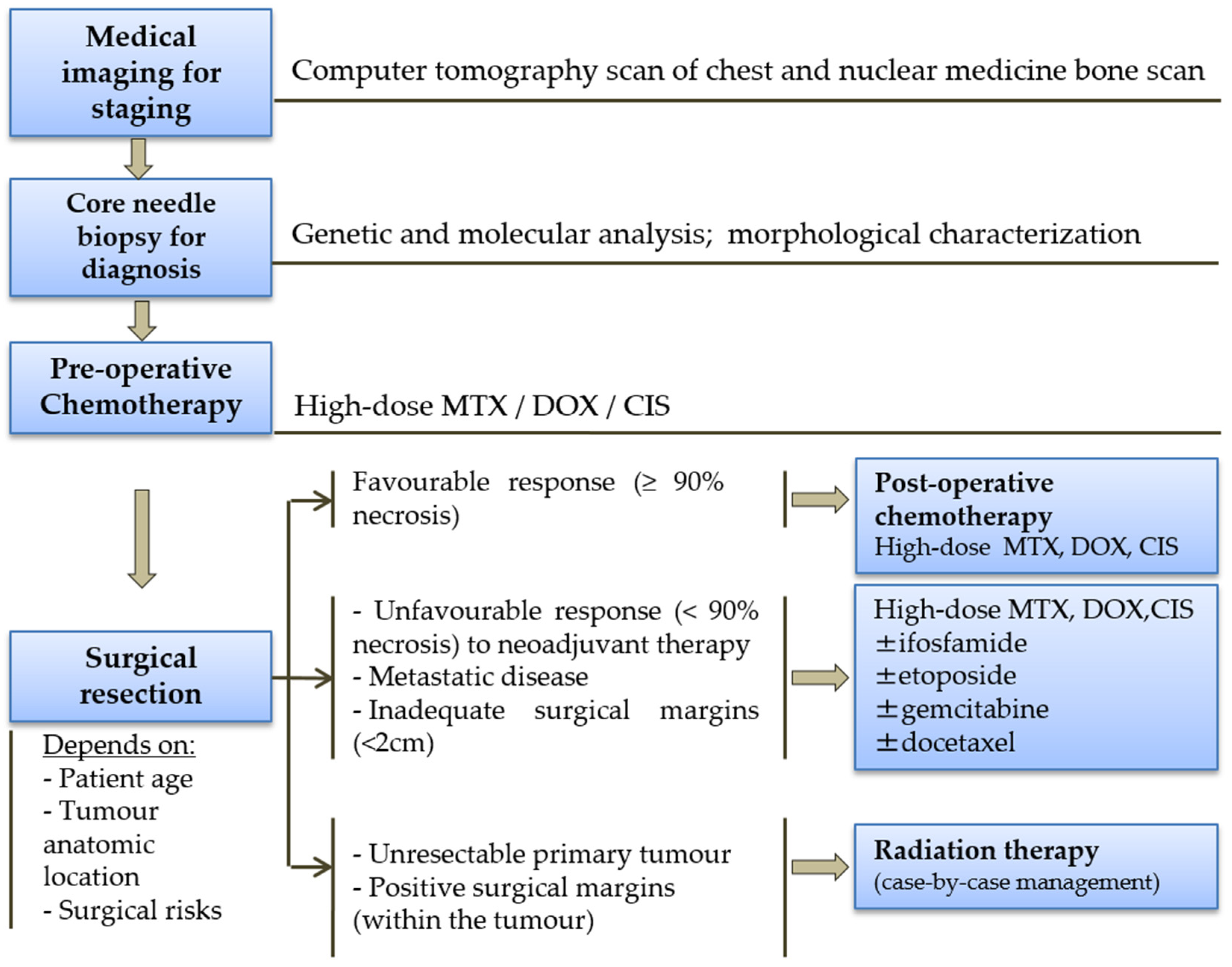
Therapy for Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer With Driver Alterations Guidelines Pocket Guide - Guideline Central

Immunohistochemical scoring of CD38 in the tumor microenvironment predicts responsiveness to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma

2023 ASPHO Conference Paper and Poster Index - 2023 - Pediatric Blood & Cancer - Wiley Online Library

Role of Nrf2 and mitochondria in cancer stem cells; in carcinogenesis, tumor progression, and chemoresistance - ScienceDirect

PDF) CD24+/CD38- As new prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer

A Role for NF-κB in Organ Specific Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Inflammation and tumor progression: signaling pathways and targeted intervention

Mitochondria in oral cancer stem cells: Unraveling the potential drug targets for new and old drugs - ScienceDirect

Volume 8, issue 1 Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine
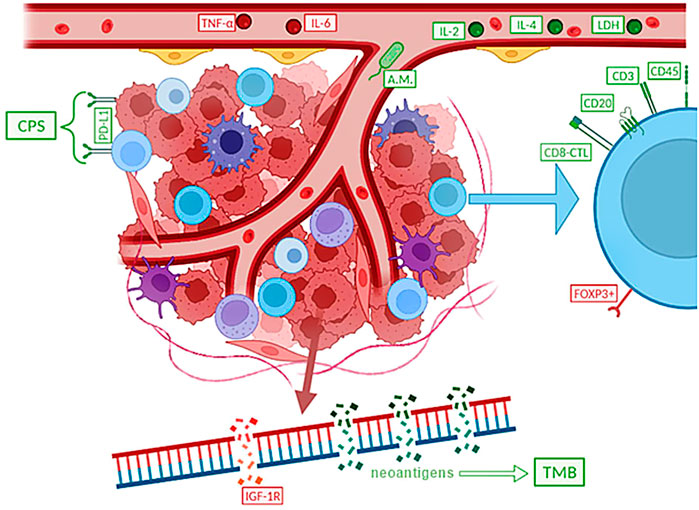
POR Potential predictors of immunotherapy in small cell lung cancer

PDF) OP9 Predictive value of CD24 and CD44 for response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and prognosis in patients with primary breast cancer

Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market report 2023-2033 - Wissen Research

High CD133 Expression in the Nucleus and Cytoplasm Predicts Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer