Figure 5 from Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes

FIGURE 5 | Electrochemical properties of CoP-350, Ru-CoP-1-350, Ru-CoP-2-350 and Pt/C for the HER in 1M KOH. (A,B) HER polarization curves, (C) Tafel plots, (D) Nyquist plots. All measurements were carried out with a fixed catalyst loading of ∼0.3mg cm−−2 on a GCE. - "Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes Derived From a Prussian Blue Analog for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution"

Transition metal phosphides as cardinal electrocatalytic materials for alkaline hydrogen production - ScienceDirect

Transition Metal Phosphide As Cocatalysts for Semiconductor-Based Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction

a) XRD patterns of Co@N-C and Mo/Co@N-C hybrids. b) Low-and c)
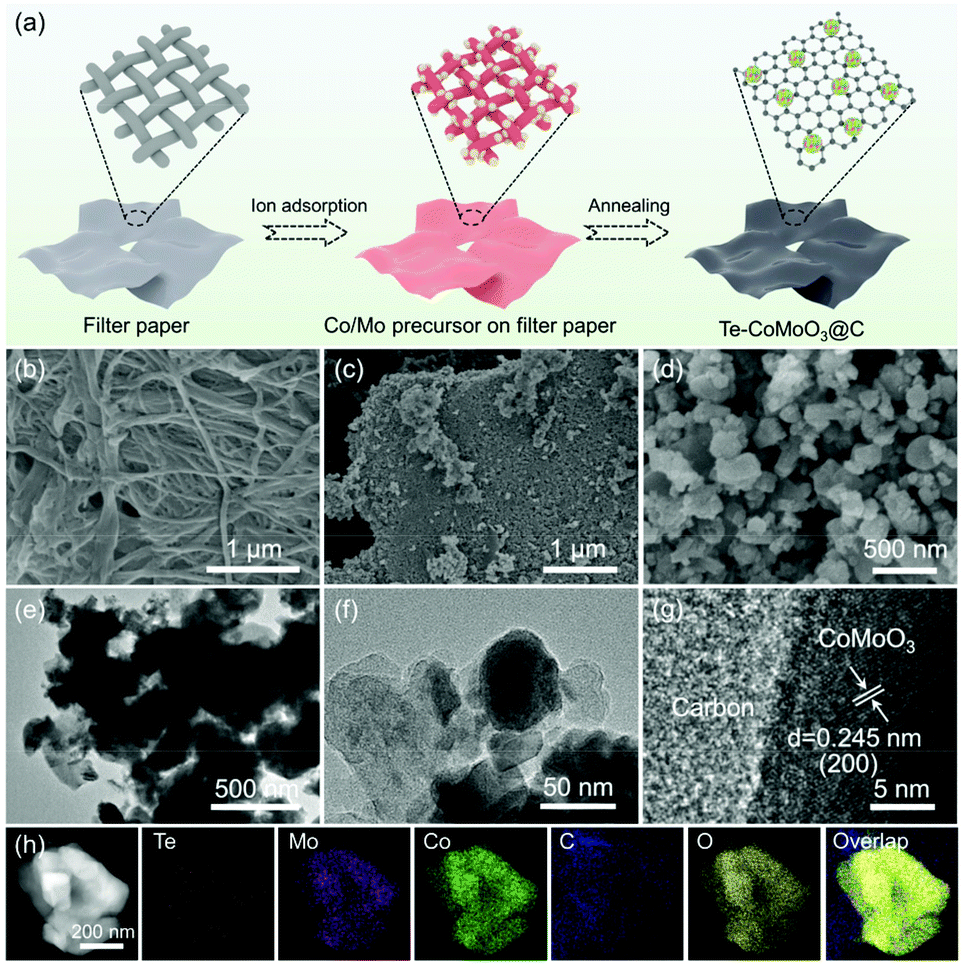
Electronic modulation of cobalt–molybdenum oxide via Te doping embedded in a carbon matrix for superior overall water splitting - Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2QI00753C

Emerging Multifunctional Single-Atom Catalysts/Nanozymes. - Abstract - Europe PMC

CV curves of scan rate ranging from 20 to 200 mV s −1 for (A)
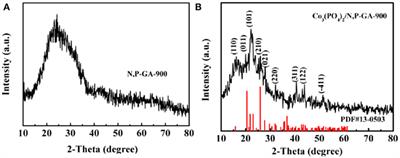
Frontiers Cobalt Phosphate Nanoparticles Embedded Nitrogen and Phosphorus-Codoped Graphene Aerogels as Effective Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction

Figure 3 from Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes Derived From a Prussian Blue Analog for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution

Figure 1 from Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes Derived From a Prussian Blue Analog for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution